Where Are Rigid Flex Circuit Boards Used?
Rigid Flex Circuit Boards
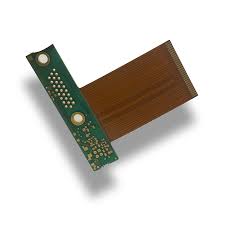
Rigid flex circuit boards combine the flexibility of flexible PCBs with the structural integrity of rigid printed circuit boards. These hybrid circuits are used in a wide variety of applications, including wearables and other “smart” products that require durability as well as adaptability. They are also often used in high-speed data communication devices, industrial equipment and power electronics.
rigid flex circuit are designed in 3D, allowing them to be bent or twisted into various shapes for different product designs. This is important for a number of reasons, including improved signal transmission and reducing the overall size of the final product. In addition, the rigid PCB sections allow these circuits to withstand mechanical stress and vibration.
Despite their increased reliability, these circuits can still be difficult to fabricate. The manufacturing process requires specialized tools and careful engineering. This can be especially challenging if you’re designing a complex board that includes both rigid and flexible sections. It’s important to work with experienced engineers or PCB manufacturing designers to ensure that your design is ready for fabrication.
Where Are Rigid Flex Circuit Boards Used?
In the right hands, rigid-flex circuits can be a great option for a variety of projects. The conductive materials in rigid-flex circuits are much thinner than traditional PCBs, allowing for more connections and better performance in a smaller package. This can be especially helpful for electronic devices that need to fit into tight spaces or operate in harsh environments. Rigid-flex circuits can also reduce assembly costs, as they eliminate the need for connector cables between rigid circuits. Connectors can add to the total assembly cost and increase the complexity of the final device.
A typical flex circuit is made of an insulating material, such as polyimide or polyester film, on which copper foil is etched to form the circuit paths. A coverlay is then applied, which protects the circuit from moisture and dirt. The outer layers of the flex circuit can be plated with either through hole or surface mount components.
When used in a flexible application, rigid-flex circuits can provide significant weight savings. These circuits are also more durable than flexible printed circuit boards, making them a good choice for wearables and other products that need to endure harsh conditions. However, rigid-flex circuits can still be prone to failure if they are not designed properly.
One of the most common challenges is ensuring that there are no issues with signal transmission between the rigid and flexible portions of the circuit. Incorrect layer transitions can cause impedance mismatches and other problems. Another challenge is ensuring that heat generated by the rigid sections is adequately dissipated.
Fortunately, these issues can be overcome with proper planning and verification during the design stage. By ensuring that your design is ready for fabrication and assembly, you can minimize the chances of encountering trouble with your rigid-flex circuits. This can help you save time and money during the manufacturing process and get your product to market sooner. By following these tips, you can ensure that your rigid-flex circuits are built on schedule and meet all of your requirements.